Sustainable Development is a holistic approach to growth and progress that seeks to address the needs of the present generation without jeopardizing the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The concept emphasizes the importance of balancing economic, social, and environmental considerations to create a harmonious and lasting development framework.
The most widely recognized definition of Sustainable Development was presented by the Brundtland Commission in its seminal report, “Our Common Future” (1987). According to this definition, Sustainable Development involves meeting the requirements of the present while safeguarding the capacity of future generations to fulfill their own needs. It underscores the interconnectedness of economic prosperity, social equity, and environmental sustainability.
Key principles of Sustainable Development include:
- Inclusivity: Sustainable Development aims to benefit all members of society, ensuring that no one is left behind. It addresses issues of poverty, inequality, and social justice to create a more equitable world.
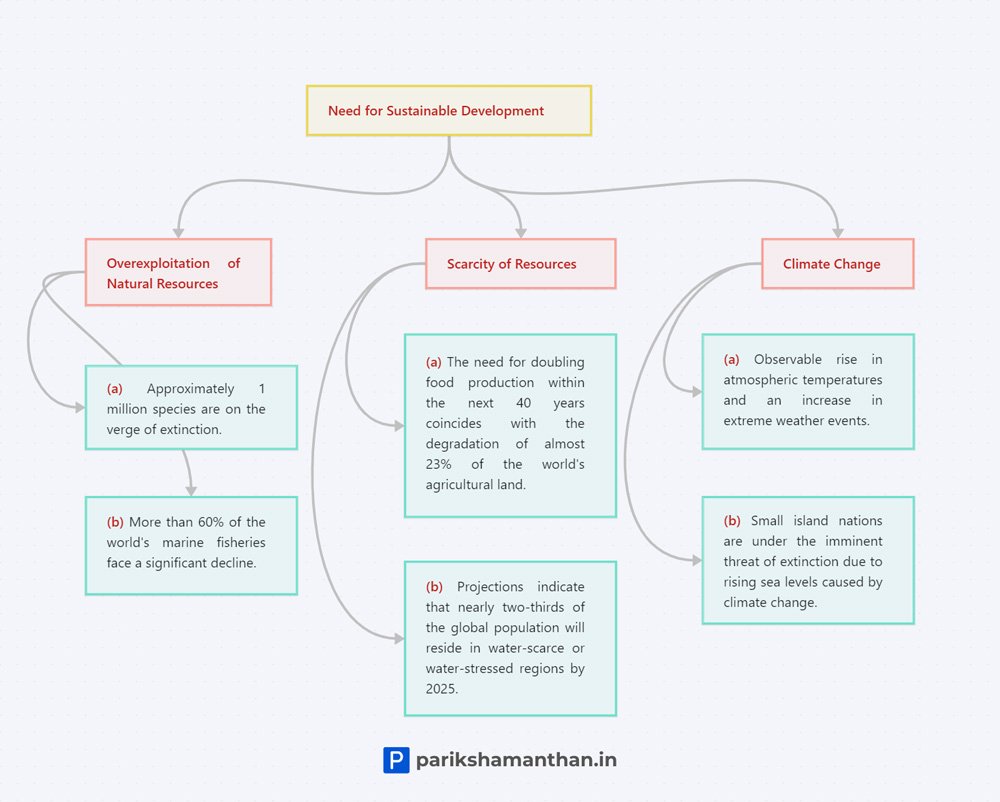
- Environmental Resilience: It recognizes the finite nature of natural resources and advocates for responsible and sustainable resource management. This includes efforts to mitigate climate change, protect biodiversity, and prevent environmental degradation.
- Economic Prosperity: Sustainable Development seeks to foster economic growth that is not only robust but also inclusive and mindful of its environmental impact. It encourages innovation and responsible business practices.
- Inter-generational Equity: The concept emphasizes the need to consider the long-term consequences of present actions on future generations. It encourages practices that leave a positive legacy for those who come after us.
- Global Collaboration: Achieving Sustainable Development requires collaborative efforts at local, national, and global levels. International cooperation is crucial for addressing global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and inequality.
- Resilience and Adaptability: Sustainable systems are designed to withstand shocks and adapt to changing circumstances. This involves building resilient communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
Core Elements of Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development is a multidimensional concept that integrates economic growth, social inclusion, and environmental protection. These core elements are interconnected and must be harmonized to create a balanced and resilient framework for development.
- Economic Growth:
Sustainable economic growth is a fundamental pillar of sustainable development. It goes beyond traditional measures of GDP to encompass a more comprehensive and inclusive approach to wealth creation. This involves fostering economic activities that benefit all members of society, ensuring that prosperity is shared and not at the expense of environmental degradation. - Social Inclusion:
Social sustainability is about creating a society where everyone has equal opportunities and access to resources. It encompasses gender equality, community development, and the preservation of diverse cultures. Achieving social sustainability involves addressing issues of inequality, promoting education and healthcare, and ensuring a reasonable and fairly-distributed quality of life for people around the world. - Environmental Protection:
Environmental sustainability is a key component of sustainable development, aiming to protect and preserve the natural world. It emphasizes the responsible use of resources, conservation of biodiversity, and mitigation of environmental degradation. Actions such as investing in renewable energy, water conservation, sustainable mobility, and innovation in construction contribute to environmental sustainability.
Environmental Sustainability:
- Nature Conservation: Prevents the exploitation of nature as an unlimited resource, emphasizing protection and rational use.
- Renewable Energy: Investments in sustainable energy sources to reduce reliance on finite fossil fuels.
- Water Conservation: Practices and technologies aimed at efficient water use to ensure its availability for future generations.
- Sustainable Mobility: Promoting eco-friendly transportation methods to reduce environmental impact.
- Innovation in Construction: Adopting sustainable practices and materials in architecture and construction.
Social Sustainability:
- Gender Equality: Ensuring equal opportunities and rights for people of all genders.
- Community Development: Fostering the growth and well-being of communities through inclusive initiatives.
- Cultural Preservation: Protecting and promoting diverse cultures for a richer global tapestry.
- Quality of Life: Striving for a balanced and fairly-distributed quality of life for everyone.
Economic Sustainability:
- Equal Economic Growth: Promoting inclusive economic growth that benefits all segments of society.
- Wealth Generation: Generating wealth without compromising environmental integrity.
- Resource Distribution: Ensuring equitable distribution of economic resources.
- Poverty Eradication: Aiming to eliminate poverty in all its forms and dimensions.
Here is the Global Initiatives on Sustainable Development organized in a table with chronological order:
| Year | Event/Initiative | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1971 | Ramsar Convention | Convention on Wetlands. |
| 1972 | The World Heritage Convention | Identifies and conserves cultural and natural heritage. |
| 1972 | Stockholm Conference | First step towards global environmental concerns. Resulted in Stockholm Declaration and set up UNEP in 1972. |
| 1973 | CITES | Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora. |
| 1979 | CMS | Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals. |
| 1985 | Vienna Convention | Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer. |
| 1987 | Montreal Protocol | Addresses substances depleting the ozone layer. |
| 1989 | Basel Convention | Controls the transboundary movement of hazardous waste. |
| 1992 | The Earth Summit | Held in Rio de Janeiro, resulted in documents like UNFCCC, Convention on Biological Diversity, Forest Principles, Rio Declaration, Agenda 21. |
| 1992 | Convention on Biological Diversity | Aims to conserve biodiversity. |
| 1993 | Global Tiger Forum | International forum for tiger conservation. |
| 1994 | UN Convention to Combat Desertification | Addresses desertification and drought. |
| 1997 | Kyoto Protocol | An international treaty to address climate change. |
| 1998 | Rotterdam Convention | Manages hazardous chemicals and pesticides. |
| 2001 | Stockholm Convention | Deals with persistent organic pollutants. |
| 2002 | Rio +10 (WSSD) | World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg, a 10-year assessment of Rio outcomes. |
| 2013 | Minamata Convention | Addresses mercury pollution. |
| 2015 | Paris Agreement | International treaty on climate change. |
| Various | Climate Change Mitigation Strategies | Includes Carbon sequestration, Carbon sink, Carbon Credit, Carbon trading, Carbon offsetting, Carbon Tax, Geo-engineering. |
| Various | UNEP | United Nations Environment Programme. |
| Various | UN Commission on Sustainable Development | UN body focused on sustainable development. |
| Various | UNCLOS | United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. |
| Various | Climate Finance Architecture | Includes Green Climate Fund (GCF), Adaptation Fund (AF), and Global Environment Facility (GEF). |
| Various | (REDD and REDD+) | Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation. |
| Various | The Clean Development Mechanism | Reduces GHGs emissions through efficient technologies. |
| Various | Global Alliance for Climate-Smart Agriculture (GACSA) | International alliance for climate-smart agriculture. |
| Various | Partnership for Action on Green Economy (PAGE) | Collaborative effort for a green economy. |
Stay Reading!







