A botanical garden is a dedicated space for the cultivation and study of living plants, serving educational and research purposes in the field of botany. Botanical gardens stand as living repositories of plant diversity, contributing to scientific advancements, conservation efforts, and public awareness of the botanical world. Botanical gardens play a crucial role in ex situ conservation of biodiversity. Ex situ conservation involves the conservation of biological diversity outside the natural habitats.
Table of Contents
Botanical Garden Definition:
A botanical garden is a curated and well-maintained space dedicated to the cultivation, study, and display of a diverse range of plants, often organized by their scientific, horticultural, ecological, or cultural significance. These gardens serve various purposes, including scientific research, education, conservation, and public enjoyment. Key features of botanical gardens include the systematic arrangement of plants, the documentation of plant collections, and the facilitation of research and educational activities related to plant life.
Botanical gardens typically house an extensive collection of plant species, including native and exotic plants, herbs, trees, shrubs, and flowers. The layout of the garden is often organized to showcase different plant families, geographical regions, or ecological themes. In addition to plant collections, botanical gardens may include specialized areas such as herbaria, seed banks, greenhouses, and educational facilities.
- History of Botanical Garden: The concept dates back to ancient times, where plants with economic and medicinal value were cultivated. Ancient Indian history reflects the cultivation of plants for medicinal and ornamental purposes around temples.
- Global Evolution: The oldest botanic gardens, including those in Pisa, Padua, and Florence (established in the 16th century), initially focused on studying medicinal and fossil plants. The 16th and 17th centuries witnessed a surge in botanical learning, leading to the rapid development of study institutes and botanical gardens worldwide.
- International Presence: Presently, there are over 500 botanical gardens worldwide, emphasizing the global significance of these institutions in advancing botanical knowledge.
- Indian Initiatives: The first botanical garden in India emerged in Bombay in 1830, initiated by the agricultural society. Subsequently, the establishment of botanical gardens in Madras (1838), Ootacamund in the Nilgiri hills, Nainital, and Lloyd Botanic Gardens in Darjeeling followed suit.
- Educational Focus: Botanical gardens serve as vital educational tools, providing a platform for botanical teaching and research. They play a crucial role in familiarizing students and researchers with plant diversity and characteristics.
- Medicinal Plant Legacy: Historical gardens had a strong emphasis on the cultivation of medicinal plants, contributing to the understanding of their properties and uses.
- Cultural Influences: Various civilizations, including the Romans, Chinese, Persians, and Aztecs, showcased a keen interest in gathering and growing plants for diverse purposes, laying the foundation for botanical practices.
- Renaissance Impact: The Renaissance period (16th-17th centuries) marked a significant shift, with increased attention given to the study and cultivation of plants. This period witnessed the establishment of renowned botanical institutions.
- Indian Expansion: The botanical garden landscape in India expanded with the establishment of gardens in diverse locations, highlighting the nation’s commitment to botanical education and research.
Objectives of Botanical Gardens
The primary objectives of botanical gardens include:
- Conservation: Botanical gardens contribute to the conservation of plant diversity, particularly for endangered and rare species, through cultivation and preservation efforts.
- Education: These gardens serve as educational institutions, providing a platform for learning about plant biology, ecology, and conservation. They often host educational programs, workshops, and guided tours for the public.
- Research: Botanical gardens support scientific research in plant taxonomy, physiology, ecology, and genetics. Researchers use these facilities to study and better understand plant life.
- Recreation and Public Engagement: Botanical gardens offer a tranquil and aesthetically pleasing environment for visitors. People can enjoy the beauty of diverse plant species while learning about their characteristics and ecological roles.
- Horticultural Practices: Botanical gardens often engage in horticultural practices, including plant breeding, landscaping, and the development of new cultivars. This expertise is often shared with the public and the broader horticultural community.
- Biodiversity Documentation: Botanical gardens maintain comprehensive records of their plant collections, contributing to the documentation of global plant biodiversity. These records can aid in plant conservation and research efforts.
Importance of Botanical Garden Short Note:
Scientific and Educational Role:
- Hub for Scientific Exploration: Botanical gardens serve as centers for scientific research, providing a platform for the study of diverse plant species.
- Educational Institutions: They play a crucial role in education, offering opportunities for students, researchers, and the public to learn about plant diversity, taxonomy, and ecological systems.
Pharmaceutical Significance:
- Medicinal Plant Resources: Botanical gardens contribute significantly to the pharmaceutical field by cultivating and studying medicinal plants. They serve as repositories of valuable plant resources for pharmaceutical research and development.
Horticultural Impact:
- Plant Cultivation and Propagation: These gardens serve as horticultural centers, cultivating and propagating a wide array of plant species. They contribute to the development of horticultural techniques and the conservation of rare and endangered plants.
Public Recreational Spaces:
- Aesthetic and Relaxing Environments: Botanical gardens are designed as pleasant public spaces, offering aesthetically pleasing landscapes for visitors. They serve as recreational areas where people can connect with nature and appreciate the beauty of diverse plant life.
Biosystematic Studies:
- Living Plant Collections: Botanical gardens keep living plant collections that provide essential material for biosystematic studies. These collections contribute to the understanding of plant taxonomy, morphology, and evolutionary relationships.
Research Stations:
- Native and Exotic Flora Studies: Botanical gardens function as research stations, facilitating studies on both native and exotic flora. Researchers conduct in-depth investigations into the ecological, genetic, and physiological aspects of plant species.
Seed and Plant Material Supply:
- Contributions to Botanical Studies: Many botanical gardens supply seeds and plant materials to researchers for botanical studies. This practice supports ongoing research and aids in the documentation of plant diversity.
Documented Collections:
- Authenticated Taxa: Botanical gardens often develop documented collections of authenticated taxa, providing a reliable resource for researchers and educators. These collections contribute to the accuracy and authenticity of botanical knowledge.
Botanical gardens, with their multifaceted roles, stand as invaluable institutions that not only preserve plant diversity but also contribute significantly to scientific advancements, education, and public engagement with the natural world.
Famous Botanical Gardens in India | Botanical Garden in India
Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden:
- Location: Howrah Shibpur, near Kolkata, India
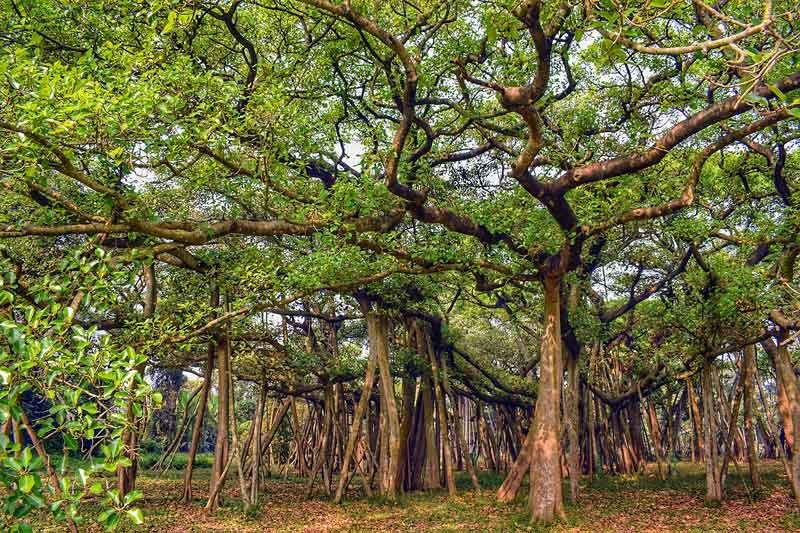
- Description: Established in 1787 by Robert Kyd, the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata spans 273 acres, making it one of South Asia’s largest and oldest botanical gardens. Renowned for its rich biodiversity, it houses over 12,000 rare plants, with a notable attraction being the 250-year-old great banyan tree, covering 3.7 acres. Despite partial damage from cyclones, it stands tall and holds a Guinness World Record for the world’s second most extensive canopy. The garden features diverse sections, including glasshouses, greenhouses, and a cactus house, along with an artificial lake for boating.
- The Great Banyan Tree is a famous banyan tree (Ficus benghalensis) located in the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in India. This magnificent tree is one of the most notable attractions in the botanic garden and holds historical and botanical significance.
- Website: For more information visit – wikipedia

Lalbagh Botanical Garden:
- Location: Bangalore, India
- Description: Situated in downtown Bangalore and sprawling over 240 acres, Lalbagh Botanical Garden is a renowned attraction commissioned by Haidar Ali and completed by Tipu Sultan. Boasting over 1,850 species of rare and exotic plants, including varieties from Afghanistan, Persia, and France, it’s a horticultural haven. The Glass House, a focal point, hosts biannual flower shows, attracting visitors during Republic Day and Independence Day celebrations. The garden features a striking rock formation, possibly dating back 3,000 million years, providing a panoramic view. Other attractions include a lake, Pigeon House, Floral Clock, Lecture Hall, Deer Paddock, and more, offering a blend of natural beauty and cultural events.
- Website: https://karnatakatourism.org/tour-item/lalbagh-botanical-garden/
TNAU Botanical Garden:
- Location: Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
- Description: The Tamil Nadu Agricultural University (TNAU) Botanical Garden, established in 1925, stands as one of the largest botanical gardens in India, covering an expansive 300 acres. Affiliated with the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, it serves as a significant educational hub, fostering awareness about plant conservation among students and the public. The garden boasts a remarkable collection of rare and endangered plant species, medicinal plants, and fruit trees. Visitors can navigate well-maintained pathways through various sections, including a bamboo garden, palm garden, rock garden, and cactus house. The garden functions as a living laboratory, offering valuable learning opportunities for students, researchers, and botanical enthusiasts. Each year, a flower exhibition in January adds to the garden’s allure, providing a visual delight and knowledge-sharing platform. TNAU Botanical Garden represents a harmonious blend of beauty and educational richness, making it one of India’s premier botanical destinations.
- Website: www.tnau.ac.in
National Botanical Research Institute:
- Location: Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India
- Description: Established in 1978 and sprawling across 25 hectares, the National Botanical Research Institute in Lucknow is one of the largest botanical gardens in India. Also known as Sikandar Bag, the garden features a massive library, two laboratories, and a herbarium. Flower exhibitions are organized biannually in January and November, providing visitors with the opportunity to witness a diverse array of flowers and purchase saplings and seeds. Emperor Nawab Saadat Ali Khan originally planned this garden, and it stands out for its rare dry flower arrangements, a distinctive feature among Indian botanical gardens. The institute boasts an extensive plant collection, attracting numerous visitors to explore its lush lawns, cactus house, conservatory, lily pools, and multiple rose gardens.
- Website: www.nbri.res.in
Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Botanical Garden:
- Location: Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
- Description: Established in 1969 and sprawled across approximately 80 hectares at the foothills of the Zabarwan Range, Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Botanical Garden in Srinagar is a tribute to India’s first prime minister, Jawaharlal Nehru. The garden comprises four main sections: Research Centre, Plant Introduction Section, Recreational Centre, and Botanical Garden. Known for its breathtaking landscapes, diverse plant species, and serene ambiance, the garden features a lake, a greenhouse, rock gardens, and themed gardens that are must-visit attractions. The 17-hectare lake offers opportunities for paddle boating, and the garden is adorned with over 300 species of rare flowers, adding vibrant hues to the surroundings. Overlooking Dal Lake, the garden provides a picturesque setting for photography, leisurely strolls, and picnics.
Lloyd’s Botanical Garden:
- Location: Darjeeling, West Bengal, India
- Description: Established in 1878, Lloyd’s Botanical Garden in Darjeeling is a scenic destination named after the renowned botanist William Lloyd. Serving as a hub for plant conservation and research, the garden focuses on promoting the native flora of the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region. Situated at an elevation of approximately 1,800 m, it boasts a vast collection of Himalayan plants. Covering 40 acres, the garden showcases over 150 species of cactus and a variety of trees arranged in well-maintained sections. The rock garden, featuring creative rock formations amid diverse plants and flowers, adds to the charm. Easily accessible from downtown Darjeeling, a short taxi ride takes you to this botanical haven, offering a perfect vantage point to appreciate the surrounding areas.
- Website: For more information visit – wikipedia
Au Jardin Zoologique, Pondichèry:
- Location: Pondicherry, India
- Description: Established in 1826, the Botanical Garden, or Jardin Botanique, in Pondicherry, India, is a serene and elegant French garden designed to provide a peaceful retreat from the heat. The entrance, showcasing grand French architecture, welcomes visitors to a world of tranquility and lush greenery. With approximately 1500 plant varieties meticulously arranged in 30 sections, the garden features giant trees and fossil plants as its highlights. The diverse collection includes endangered and exotic plant species, making it a haven for nature enthusiasts. Beyond its botanical richness, the Pondicherry Botanical Garden serves as a holistic destination for tourists, offering opportunities for relaxation and entertainment. The garden’s primary objective is to promote education and raise awareness about plant conservation. It hosts flower shows, training workshops, and plant sales, contributing to its role as a multifaceted hub for nature appreciation and environmental education.
- Website: For more information visit – https://agri.py.gov.in/bggarden.html
List of Botanical Garden in India
| Serial No. | Botanical Garden Name | Location | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Assam State Zoo-cum-Botanical Garden | Guwahati, Assam | Assam |
| 2 | Botanical Garden Sarangpur | Chandigarh | Chandigarh |
| 3 | Sanjay Gandhi Jaivik Udyan | Patna, Bihar | Bihar |
| 4 | Botanical garden Vaghai | Saputara, Gujarat | Gujarat |
| 5 | R. B. Botanical Garden and Amusement Park | Gujarat | Gujarat |
| 6 | The Garça Branca Ayurvedic Botanical Garden | Loutolim, Goa | Goa |
| 7 | Curzon Park | Mysore, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 8 | Pilikula Arboretum, Pilikula Nisargadhama | Mangalore, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 9 | Regional Museum of Natural History Mysore | Mysore, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 10 | University of Mysore Botanic Garden | Mysore, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 11 | Prof. Nagaraj Botanical Garden | Kalaburgi, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 12 | Lalbagh | Bangalore, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 13 | Mysore Zoo | Mysore, Karnataka | Karnataka |
| 14 | Jawaharlal Nehru Tropical Botanic Garden and Research Institute | Trivandrum, Kerala | Kerala |
| 15 | Vellayani Agricultural College | Trivandrum, Kerala | Kerala |
| 16 | Malampuzha Garden | Palakkad, Kerala | Kerala |
| 17 | Empress Garden | Pune, Maharashtra | Maharashtra |
| 18 | Odisha State Botanical Garden | Nandankanan, Bhubaneswar, Odisha | Odisha |
| 19 | Botanical Garden Guru Nanak Dev University | Amritsar, Punjab | Punjab |
| 20 | Botanical Garden Punjabi University | Patiala, Punjab | Punjab |
| 21 | Auroville Botanical Gardens | Auroville, Tamil Nadu | Tamil Nadu |
| 22 | Botanic Gardens – Tamil Nadu Agricultural University | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu | Tamil Nadu |
| 23 | Government Botanical Gardens | Ootacamund, Nilgiris district, Tamil Nadu | Tamil Nadu |
| 24 | The Institute of Forest Genetics and Tree Breeding | Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu | Tamil Nadu |
| 25 | Semmozhi Poonga | Chennai, Tamil Nadu | Tamil Nadu |
| 26 | Botanical Garden | Hyderabad, Telangana | Telangana |
| 27 | NTR Garden | Hyderabad, Telangana | Telangana |
| 28 | Botanical Garden of India Republic | Noida, Uttar Pradesh | Uttar Pradesh |
| 29 | Jhansi Botanical Garden | Jhansi, Uttar Pradesh | Uttar Pradesh |
| 30 | Saharanpur Botanical Garden | Saharanpur, Uttar Pradesh | Uttar Pradesh |
| 31 | Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden | Shibpur, Kolkata, West Bengal | West Bengal |
| 32 | Agri Horticultural Society of India | Alipore, Kolkata, West Bengal | West Bengal |
| 33 | Garden of Medicinal Plants | North Bengal University, West Bengal | West Bengal |
| 34 | Lloyd’s Botanical Garden | Darjeeling, West Bengal | West Bengal |
| 35 | Narendra Narayan Park | Cooch Behar, West Bengal | West Bengal |
Top 10 Largest Botanical Garden In World
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew England (London, UK):
- Location: London, England
- Description: Established in 1840, Kew Gardens is not only one of the oldest but also the largest collection of living plants globally. Situated in the London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, it boasts over 30,000 plant species and a herbarium with seven million preserved specimens. Recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site, it features iconic glasshouses and serves as a hub for botanical research and conservation.
- Website: www.kew.org
Singapore Botanic Gardens (Singapore):
- Location: Singapore
- Description: Established in 1859, the Singapore Botanic Gardens sprawls over 183 acres, offering a tropical haven with a rich heritage. The National Orchid Garden, a prominent feature, houses an impressive collection of over 1,000 orchid species and 2,000 hybrids across its hilly three-hectare expanse.
- Website: www.nparks.gov.sg/sbg
Missouri Botanical Garden (St. Louis, USA):
- Location: St. Louis, USA
- Description: Established as one of the oldest botanical institutions, the Missouri Botanical Garden is renowned for extensive botanical research and global conservation initiatives. Boasting 50 diverse gardens and plant collections, it stands as a testament to botanical excellence.
- Website: www.nybg.org
Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden (Cape Town, South Africa):
- Location: Cape Town, South Africa
- Description: Situated against the backdrop of Table Mountain, Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden, established in 1913, spans 89 acres and is dedicated to preserving South Africa’s unique flora. Notably, it exclusively cultivates indigenous plants, contributing significantly to local flora conservation.
- Website: www.sanbi.org/gardens/kirstenbosch
Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney:
- Location: Sydney, Australia
- Description: The Royal Botanic Gardens in Sydney, established in 1816, stands as a major botanical garden in the heart of the city. It holds the distinction of being the oldest scientific institution in Australia and is globally recognized as a significant historical botanical establishment.
- Website: www.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au
Botanischer Garten München:
- Location: Munich, Germany
- Description: Munich’s first botanical garden, now known as the “old botanical garden,” was founded in 1809 according to designs by Friedrich Ludwig von Sckell near Karlsplatz. Though the original site is still visible, the garden has evolved. It spans 18 hectares and cultivates approximately 14,000 species.
- Website: www.botmuc.de
Jardin Botanique de Montreal:
- Location: Montreal, Canada
- Description: Established in 1931, the garden utilizes both indoor and outdoor spaces, offering visitors a year-round treasure. With a diverse range of plants and exhibits, it serves as a botanical haven in Montreal.
- Website: www.espacepourlavie.ca/jardin-botanique
Hawaii Tropical Botanical Garden:
- Location: Pāpa’ikou, Hawaii
- Description: Established in 1984, this 17-acre nonprofit botanical garden and nature preserve offer a scenic route spanning 4 miles. Nestled in a valley opening to Onomea Bay, it features streams, waterfalls, and an ocean-side boardwalk, showcasing over 2,000 plant species.
- Website: www.htbg.com
Orto Botanico di Padova:
- Location: Padua, Italy
- Description: Established in Padua, Italy, this botanical garden holds historical significance as the world’s oldest academic botanical garden. Founded in 1545, it serves as a center for research and education, fostering the growth of diverse plant species.
- Website: www.ortobotanicopd.it
Longwood Gardens:
- Location: Philadelphia, USA
- Description: Longwood Gardens, situated in Philadelphia, USA, is a renowned horticultural display garden spanning over 1,000 acres. With a history dating back to the early 20th century, it features exquisite landscapes, conservatories, and a vast collection of plants, making it a prominent attraction for visitors.
- Website: www.longwoodgardens.org
📝 Botanical Garden PDF – Click Here to Download PDF
FAQ:
-
What is a botanical garden
A botanical garden is a meticulously curated space dedicated to the cultivation, study, and exhibition of a diverse range of plants for scientific, educational (through the use of libraries, herbaria, laboratories, and museums), and conservation purposes, providing a living collection that showcases plant diversity and supports research and public education.
-
How many botanical garden in India
There are about 122 botanical gardens recorded in India. India boasts numerous botanical gardens, with specific numbers varying across regions. Notable examples include the Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata, Lalbagh Botanical Garden in Bangalore, and the Indian Botanic Garden in Ooty.
-
Botanical garden and zoological parks have ?
Botanical gardens and zoological parks serve distinct purposes. Botanical gardens prioritize the cultivation and display of plants for conservation, research, and educational purposes. Zoological parks, on the other hand, primarily focus on the exhibition and conservation of animal species for public awareness and scientific study. These facilities accommodate both endemic (native) and exotic (foreign to the region) species, providing opportunities for scientific research and conservation efforts.
-
India’s largest botanical garden
The Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden in Kolkata, India. The gardens exhibit a wide variety of rare plants and a total collection of over 12,000 specimens spread over 109 hectares, stands as one of India’s largest botanical gardens. Its historical significance and vast plant collection make it a prominent attraction.
-
Largest botanical garden in world (World biggest botanical garden)
The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, located in London, is renowned as one of the world’s largest botanical gardens. Its vast acreage, diverse plant collections, and commitment to research contribute to its global prominence.
-
_________is the first botanical garden in india (oldest Botanical garden in india)
Acharya Jagadish Chandra Bose Indian Botanic Garden (Calcutta Botanic Garden), established in 1786, holds the distinction of being India’s first and oldest botanical garden. It has played a pivotal role in plant taxonomy, research, and conservation.
-
Why do we have greenhouse in botanical gardens
Greenhouses in botanical gardens serve the crucial purpose of creating controlled environments to support the growth of exotic or delicate plants. They are crucial for preserving exotic and delicate plants that may not thrive in the local environment.
-
What is Flora Indica, and what role did William Roxburgh play in its creation?
‘Flora Indica’ is a seminal botanical work documenting the flora of India. William Roxburgh, the Scottish botanist and served as the head of the Calcutta Royal Botanic Gardens for two decades, played a crucial role in its creation, overseeing extensive plant collections, classifications, and descriptions, contributing significantly to the understanding of India’s diverse plant life.
-
How do botanical gardens contribute to plant conservation?
Botanical gardens preserve endangered plant species, conduct research on plant genetics, and establish seed banks to safeguard biodiversity. They play a vital role in educating the public about conservation challenges and promoting sustainable practices.
-
What is the oldest botanical garden in the world?
The Botanical Garden of Padua, Italy, founded in 1545, holds the title of the oldest botanical garden still in its original location, making it a historical landmark in the field of botany.
-
How do botanical gardens support scientific research?
Botanical gardens provide controlled environments for studying plant behavior, conducting experiments, and developing sustainable agricultural practices. Researchers use these living laboratories to explore plant genetics, ecology, and medicinal properties.
-
What role do botanical gardens play in education?
Botanical gardens serve as outdoor classrooms, offering educational programs, workshops, and guided tours. They enhance public awareness about plant life, biodiversity, and environmental conservation, fostering a deeper understanding of the natural world.
-
Can you name a botanical garden known for its historical significance?
The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, in London, holds historical significance, dating back to the 18th century. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a global center for botanical research.
-
How do botanical gardens help preserve endangered plant species?
Botanical gardens establish ex situ conservation programs, cultivating and propagating endangered plants away from their natural habitats. These living collections act as insurance against extinction and contribute to species recovery and reintroduction efforts.
-
What distinguishes a botanical garden from a regular garden?
Botanical gardens prioritize scientific research, plant conservation, and education. They curate diverse plant collections, organize thematically, and often display labeled specimens for educational purposes, distinguishing them from typical gardens.
-
What is the significance of a herbarium in a botanical garden?
Herbaria house dried plant specimens systematically arranged for scientific study. They serve as reference libraries, aiding botanical research, plant identification, and taxonomy. Herbarium collections contribute crucial data to understanding plant diversity and evolution.
-
How do botanical gardens support sustainable practices?
Botanical gardens model sustainable landscaping, promote eco-friendly practices, and conduct research on plant adaptations to climate change. They play a role in advocating for environmental stewardship and encouraging sustainable choices within their communities.
-
How do botanical gardens aid in the study of plant taxonomy?
Botanical gardens house diverse plant collections, providing researchers with living specimens for taxonomic studies. By preserving plant diversity, they contribute valuable data to the classification and naming of plant species.
-
Name a botanical garden that actively engages in horticultural practices.
The Butchart Gardens in British Columbia, Canada, actively engages in horticultural practices, featuring stunning landscape designs, themed gardens, and a commitment to sustainable horticulture.
-
Can you name a botanical garden known for its extensive collection of medicinal plants?
Missouri Botanical Garden, St. Louis, USA: Home to the Peter H. Raven Library, containing one of the most comprehensive collections of botanical literature in the world, including texts on traditional medicine and pharmacognosy. The garden also boasts dedicated sections like the Henry Shaw Medicinal Plant Garden and the Doris Duke Center for Conservation Ecology, promoting research and education on medicinal plants.
-
How do botanical gardens contribute to community well-being?
Botanical gardens provide green spaces for recreation, relaxation, and physical activity, contributing to community well-being. They host events, promote mental health, and serve as hubs for environmental education and cultural activities.
-
Where is the National Cactus and Succulent Botanical Garden and Research Centre located in India?
The National Cactus and Succulent Botanical Garden and Research Centre is recognized as one of the largest cactus and succulent botanical gardens in India. Located in Panchkula, Haryana, it houses a diverse collection of these unique and resilient plant species. The garden serves as a hub for research, conservation, and public awareness about cacti and succulents.
-
What botanical destination in India boasts the largest collection of aquatic plant species?
The Malabar Botanical Garden and Institute of Plant Sciences proudly holds the title, offering a stunning array of aquatic plants and serving as a hub for botanical research and conservation.